

Max Wilbert is a passionate writer, live streaming practitioner, and has strong expertise in the video streaming industry.
Share this postThere are many different acronyms used in live streaming. RTMP, HLS, SRT and more. These generally refer to different video streaming protocols. Essentially, these protocols are technical processes that facilitate the efficient transfer of data from one program to another. In streaming, this amounts to the transference of video files to and from your encoder, streaming host, and the video player your audience views.
The protocol you choose for your video streaming can impact the quality of your stream, its latency, and its security. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each protocol can help you to make informed decisions that optimize the viewing experience for your audience.
Table of Contents
In this article, we’re going to identify and discuss the most common video streaming protocols. We’ll cover what they do and when they should be used. Furthermore, we’ll shed light on and break down all the acronyms associated with video streaming protocols. Finally, we’ll enlighten you with relevant background information so that you can better understand the relationship between a codec vs. a container format.

A video streaming protocol is necessary for live broadcasting.
A video streaming protocol is a standardized delivery method for breaking up a video into chunks, sending it to the viewer, and reassembling it. Video streaming protocols are the rules and methods that are used to break video files into small pieces . These protocols also specify methods for correcting errors during transmission and how the data is delivered to the video player on the viewer’s device.
Before we go further, let’s look a little further into the “why” behind video streaming protocols. Most digital video is designed for two things: storage and playback. This leads to two major considerations, namely small file size and universal playback.
Most video files aren’t designed for streaming, which means streaming a video involves first converting it into a streamable file. This involves breaking the video up into small chunks. These chunks then arrive sequentially and playback as they’re received. If you’re streaming live video, the source video comes in straight from a camera. Otherwise, it’s coming from a file for video-on-demand VOD content.
That is a basic explanation of how streaming protocols work. Streaming protocols can get much more complex. Many are “adaptive bitrate” protocols, for example. This technology will deliver the best quality that a viewer can support at any given time.
So if a viewer has a slow internet speed, they will be delivered a lower-quality video, and if a viewer has a faster internet speed, they will be delivered a higher-quality video.
Some protocols focus on reducing latency, or the delay between an event happening in real life and when it plays on the viewer’s screen. Some video protocols only work on certain systems, and other video protocols focus on digital rights management (DRM).
As we move through some specific video streaming protocols, we will put these and other characteristics into perspective.

Protocols, codecs, and container formats are separate facets of streaming.
Among others, one common source of confusion in the realm of streaming video relates to the difference between a video protocol and a codec.
Simply put, the term “codec” refers to video compression technology. Logically, different streaming codecs are used for different purposes. For example, Apple ProRes is among the video codecs often used for video editing. H.264 , the most common video codec, is widely used for online video.
As with codec, the term “format” can also be confusing in the context of video streaming protocols. In many cases, format simply refers to the container format of a video file. Common container formats include .mp4, .m4v and .avi.
In essence, a container format functions like a “box” that usually contains a video file, an audio file, and metadata. However, container format isn’t as central a concept for live streamers.
Let’s make a comparison to make it easier to understand the relationship between a codec, a container format, and a streaming protocol.
Imagine that you’re a merchant, and you’re transporting clothing in bulk (the clothing represents the video content):
As a content creator or broadcaster, it’s essential to consider the interplay between codecs, container formats, and streaming protocols when preparing your video for online delivery. Selecting the right combination depends on several factors, including the target audience’s device compatibility, desired video quality, and the capabilities of the streaming platform you’re using.
It’s also important to note that most video streaming protocols only support certain codecs, but we’ll get more into this later.
6 Preferred Protocols for Video Streaming
Now that you have a better idea of the purpose of video streaming protocols, let’s start our comparison with a list of the most common protocols for video streaming today. This will help you better understand the best video protocols for live streaming and videos-on-demand.
In this comparison, we’ll also offer use cases for each video protocol whenever possible.
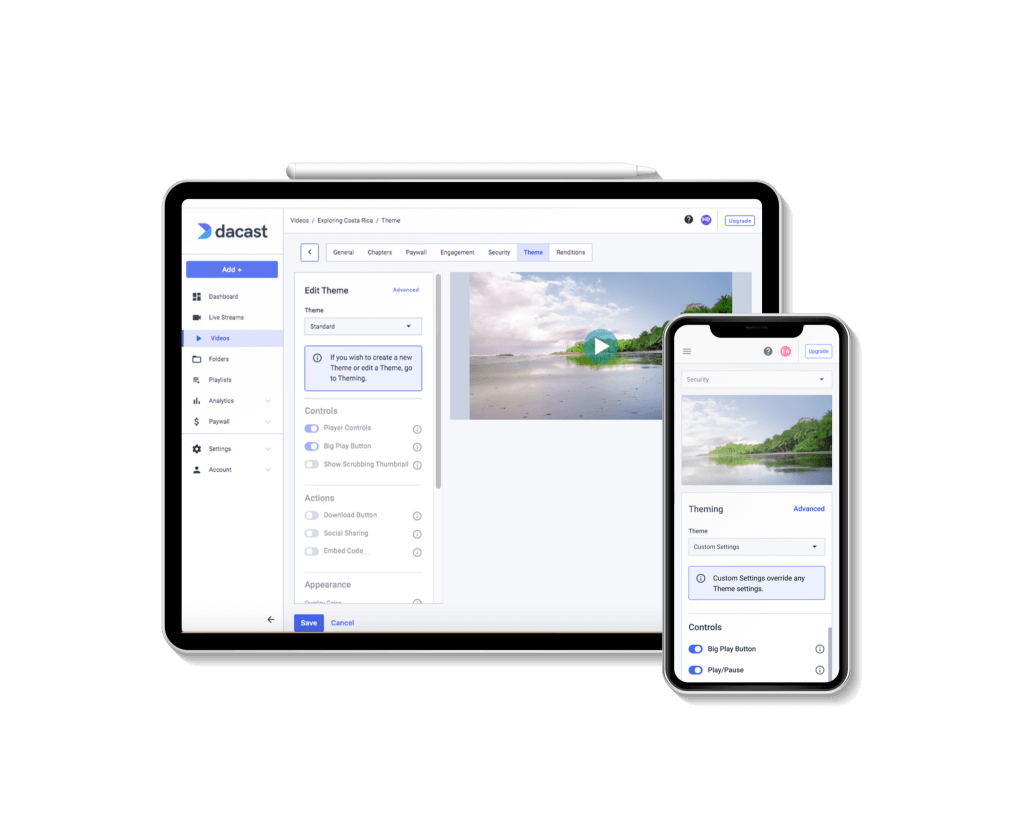
The HLS protocol, or HTTP Live Streaming, was developed by Apple and has support for media players, web browsers, mobile devices, and media servers.
The first video streaming protocol we’ll discuss is HTTP Live Streaming or HLS. Apple originally released this video protocol in 2009 to enable them to drop Flash from iPhones. Since then, HLS has become the most widely-used streaming protocol.
There are several reasons for this. First, desktop browsers, smart TVs, and both Android and iOS mobile devices all support HLS. HTML5 video players also natively support HLS streaming With so many devices supporting HLS, it is only natural that it has become one of the best video protocols for streaming video.
This allows a stream to reach as many viewers as possible, making HLS the safest protocol today for scaling a live stream to large audiences. For example, you can use this protocol to stream live video on your website with a simple embed code, and you can reach viewers on most devices.
As far as features, the HLS standard also supports adaptive-bitrate streaming, dynamically delivering the best possible video quality at any moment to each individual viewer. With recent updates, this standard now supports the latest and greatest H.265 codec, which delivers twice the video quality at the same file size as H.264 . Both formats are lossy codecs. Lossy codecs compress video files by discarding some of the data, resulting in a smaller file size but potentially lower video quality. In contrast, lossless codecs, such as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), compress video files without discarding any data, resulting in higher video quality but larger file sizes.
HLS also supports various audio codecs, including Advanced Audio Coding (AAC), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and free lossless audio codecs like FLAC for audio files.
Currently, the only downside of HLS is that latency can be relatively high. Latency is the delay one experiences between when a file is sent and the viewer receives it. With live video streaming, latency can best be described as the delay between when live content and when the viewer gets that content. However, there are methods for reducing HLS latency, helping to combat one of the few downsides to this video protocol.
HLS is the most widely-used protocol for live stream delivery because it’s robust and effective. For example, we know that few viewers will return to a site during a stream if they experience a video failure. Using a widely compatible, adaptive protocol like HLS will deliver the best possible audience experience.
HLS leverages powerful data compression algorithms, which makes it perfect for delivering high-quality video content to a broad audience across various devices and internet speeds. Owing to the strengths of HLS, Dacast has chosen HLS as its default streaming protocol to ensure a high-quality experience for its users.
Next up is the veteran video protocol: or Real-Time Messaging Protocol. Originally developed by Macromedia in the early days of streaming, the RTMP protocol is still widely used.
Today RTMP is mostly used for ingesting live streams with the help of an RTMP-enabled encoder. In plain terms, when you set up your encoder to send your video feed to your streaming platform, that video will reach the platform via the RTMP protocol. That content eventually reaches the end viewer in another protocol, usually HLS. RTMP is used together with other video streaming protocols.
RTMP is rarely used as a viewer-facing video streaming protocol like it once was. That’s because it’s dependent on the Flash plugin, which is now totally obsolete. If it is used, it is usually paired with another protocol like HLS.
RTMP is a streaming protocol that provides very low latency streams. However, because it is incompatible with the HTML5 video player, we do not recommend using RTMP for delivery. Again, the exception is for stream ingestion. For this purpose, is still one of the best options for stream ingestion. It’s robust and almost universally supported.

WebRTC is primarily used for peer-to-peer communication, specifically with web conferencing.
Web Real-Time Communications (WebRTC) is an open-source video project that is capable of streaming with real-time latency. This project was developed to support voice-over-internet protocol (VoIP), and it was purchased by Google to support Google’s video chatting tools.
WebRTC is technically a streaming project and not a streaming protocol. However, it is often lumped in with the preferred video streaming protocols since there is a lot of overlap.
WebRTC is valuable in streaming setups that require real-time latency. Peer-to-peer streaming, which is commonly called “web conferencing” or “video conferencing” is one of the top use cases of WebRTC.
Some popular software and apps that use WebRTC include Snapchat, Facebook, WhatsApp, and other social media platforms that support video chatting.
Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) is a relatively new video streaming protocol from Haivision, a leader in the online streaming industry. This open-source protocol is known for its remarkable security, reliability, compatibility, and capability of low latency streaming. It is a great real-time streaming protocol.
There are currently some limitations on streaming with SRT because other streaming hardware and software have yet to develop to support this video protocol.
SRT is the preferred protocol of many members of the SRT Alliance. This is a group of companies in the technology and telecommunications space that are dedicated to pushing SRT to the forefront of the live streaming industry because they believe it is the best protocol for streaming video.
The SRT Alliance was founded by Haivision, the same company that developed the video streaming protocol. Some major members of the SRT Alliance include Microsoft, Telestream, Alibaba Cloud, Comcast, Eurovision, and AVID.
If you are using technology that is supported by any of the SRT Alliance members, you should be able to easily incorporate SRT video streaming protocol into your streaming setup.
Perhaps a lesser-known video streaming protocol, Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) was first published in 1998. RTSP was developed to control streaming media servers in entertainment and communications systems, specifically.
In 2016, an updated RTSP 2.0 became available. Overall, it is known as a video streaming protocol for establishing and controlling media sessions between endpoints.
RTSP is similar in some ways to the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol, which we’ll cover below. However, transmitting live streaming data is not what RTSP accomplishes on its own. Instead, RTSP servers often work in conjunction with the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) and Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP) to deliver media streams. It is a real-time solution that needs to work together with other video streaming protocols.
RTSP was designed to support low-latency streaming and is a good choice for streaming use cases such as IP camera feeds (e.g. security cameras), IoT devices (e.g. laptop-controlled drone), and mobile SDKs. It is not designed for high-quality live streaming over the internet to numerous viewers.
One significant drawback, however, is there is limited native browser support for RTSP
RTMP and RTSP are both streaming protocols, meaning they are sets of rules that govern how data travels from one system of communication to another. These similar-looking acronyms are often confused with one another. If the video data you’re trying to send to your viewers is a car, then the streaming protocol is the road that the car takes to get from one place to another.
Choosing between RTMP vs. RTSP streaming protocols greatly depends on your individual business needs and how many extra steps you are willing to take to make your content playable on your website.
6. Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH)
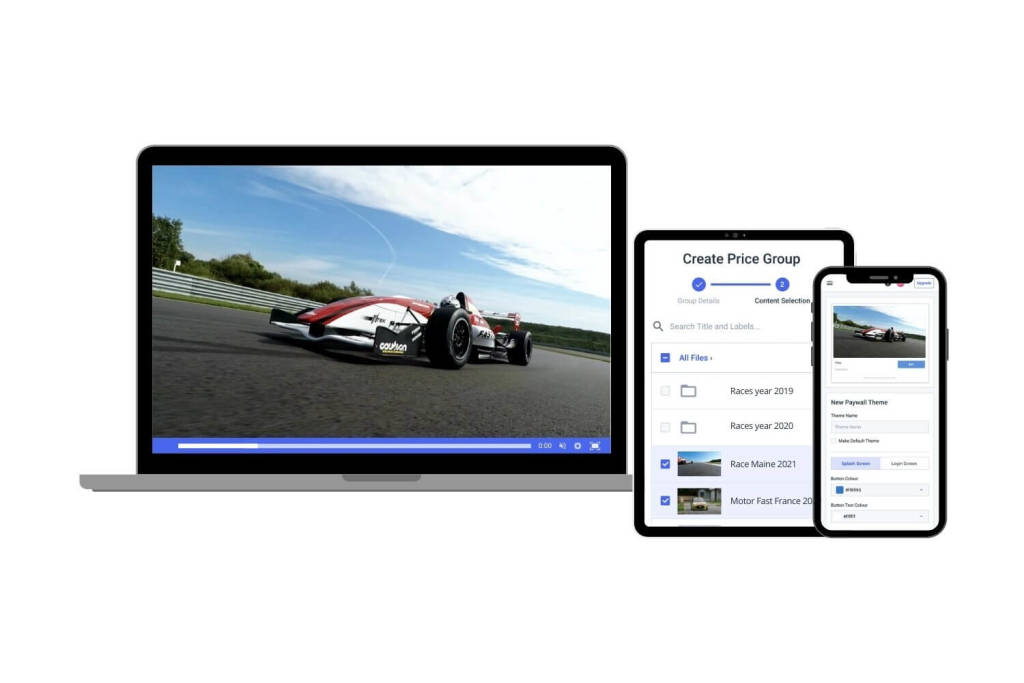
Adaptive streaming capabilities with MPEG-DASH are extremely valuable to professional broadcasters.
Last but not least, we have MPEG-DASH. While it’s not widely used yet, this video protocol has some big advantages.
First, it supports adaptive-bitrate streaming. That means viewers will always receive the best video quality that their current internet connection speed can support. This tends to fluctuate second to second, and DASH can keep up.
MPEG-DASH fixes some long-standing technical issues with delivery and compression. Another advantage is that MPEG-DASH is “codec agnostic,” meaning it can be used with almost any streaming encoding format. It also supports Encrypted Media Extensions (EME) and Media Source Extension (MSE) which are standards-based APIs for browser-based digital rights management (DRM).
These days, MPEG-DASH is only being used by a fraction of professional broadcasters as compared to HLS. For a while, experts believed that this protocol would take off, but we are yet to see that theory come into fruition.
The reason that this protocol is not incredibly popular can be attributed to compatibility (e.g. Apple Safari and iOS devices do not support it) and other related issues.
Do you know which video protocols are best for professional live streaming?
To recap, there are many video streaming protocols in existence today, and many of these can be used for live video streaming. When it comes to what protocol to use for streaming media, the answer is, it depends on your specific needs.
As we covered above, all of the protocols discussed here have specific use cases for specific broadcasters. However, when taking everything into account, HLS comes out on top, especially in terms of codec compatibility, all-device compatibility, HTML5 video player native support, and adaptive-bitrate streaming capacity.
Our takeaway recommendation here is simple: for now, most broadcasters should stick to using HLS for delivery and RTMP for ingestion. HLS is our choice for video streaming standard for the best video streaming protocol.
Of course, some users may find other protocols better for their needs. However, whether you want to stream live video on your website, do live streaming of sports events or broadcast professional events and gatherings live, HLS is generally the best way to go.
Keep an eye out for SRT and WebRTC as they make their way to the forefront of the online streaming industry in the future.
As we discussed, the video protocols you use will depend on your specific streaming setup. To give you a better understanding of how system requirements and other technology will contribute to your decision, let’s discuss the different protocol combinations you can use with YouTube.
YouTube uses an HTML5 video player, which means that HLS is the standard protocol for delivery. When it comes to ingestion on YouTube, there are four different protocol options. These include HLS, RTMP, RTMPS, HLS, and DASH.
Since we haven’t covered it already, it is worth noting that RTMPS is a variation of RTMP that has an added layer of security.
RTMP and RTMPS can be used for normal, low, and ultra-low latency streams. HLS and DASH are better for streaming in higher quality, but neither is capable of low latency streaming like RTMP and RTMPS.
RTMP is the most commonly used protocol for ingesting on YouTube.
Which protocol you use will depend on whether you value high-quality or low-latency. It will also depend on the compatibility of your streaming encoder and other broadcasting tools.
1. What is the difference between RTMP and RTMPS?
RTMP and RTMPS are both protocols used for live streaming video, but they differ in their security. RTMP stands for Real-Time Messaging Protocol and transmits data in a lightweight way optimized for speed and low latency. RTMPS, or Real-Time Messaging Protocol Secure, is a secure version of RTMP. It adds a layer of encryption using either TLS or SSL protocols to scramble the data during transmission.
2. Which is better between RTMPS and HLS?
RTMPS and HLS excel in different areas. RTMPS prioritizes low latency, making it ideal for real-time applications like live auctions or interactive gaming where a slight delay can be detrimental. However, RTMP struggles with wide device compatibility and smooth playback over fluctuating internet connections.
HLS, on the other hand, adapts to various network conditions. It allows viewers to experience smooth playback even with a weak connection. Additionally, HLS streams allow broad device support, making it a great choice for reaching a large audience. However, it introduces slight delay compared to RTMP.
3. How do I use WebRTC in my browser?
WebRTC doesn’t directly require user activation in your browser. It’s a built-in technology that websites can use to enable features like video chat and file sharing. However, you might need to grant permission to the website to access your camera and microphone.
4. Is RTSP still being used?
Yes, RTSP is still a relevant protocol, especially in video surveillance. While it may not be the most popular choice for general streaming anymore, it remains the standard for IP cameras. RTSP offers good control over the stream, allowing features like pause, play, and seeking. Additionally, its simple design makes it efficient for handling multiple streams on a server.
5. Is WebRTC free?
Yes, WebRTC is free to use. It’s an open-source project, meaning there’s no licensing fee or royalties to pay to develop web apps that use WebRTC.
While streaming protocols and related technology can be complex, they can be easily broken down into easier to understand segments. This is what we’ve tried to do in this article so that you can better understand the technological jargon.
We trust that this article has helped clarify the purpose of.a protocol for video streaming and the relationship between a video streaming protocol, vodec and container format. Equipped with this, you’ll be better able to choose the right video streaming protocol that suits your needs.
Did you know you can test high-quality HSL streaming on Dacast’s platform? With Dacast’s 14-day risk-free trial, you can test this and all the other features and functionalities without needing to commit.
Any questions? Let us know by leaving a comment below! We have experience with most kinds of live video streaming protocols, so we can probably help no matter what issues you’re experiencing. For exclusive offers and regular live streaming tips, join our LinkedIn group
Max WilbertMax Wilbert is a passionate writer, live streaming practitioner, and has strong expertise in the video streaming industry.